Definitions 1 bioreactor is a vessel in which a chemical process is carried out which involves organisms mainly microbes viruses or bacteria fungi and yeasts traditionally designated as fermenters or biochemically active substances enzymes e g derived from such organisms.
Bioreactors for animal cell culture slideshare.
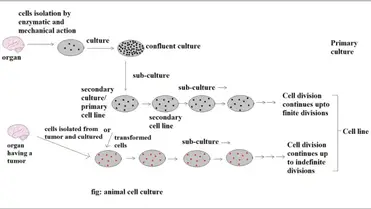
The extant bioreactors work well for cells that float such as the hemopoietic cells in which starling flow can adequately provide gases and nutrients but are limited in their utility for adherent cell types derived from solid tissues or organs.
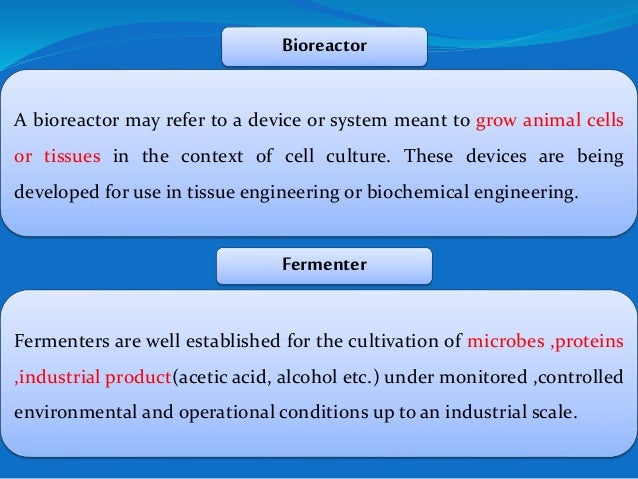
A bioreactor refers to any manufactured device or system that supports a biologically active environment.
At high cell densities the culture will be viscous and difficult to mix in airlift bioreactor.
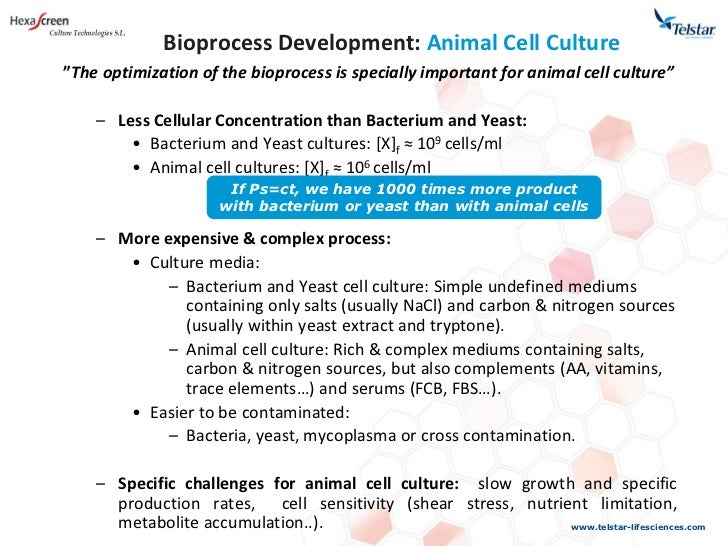
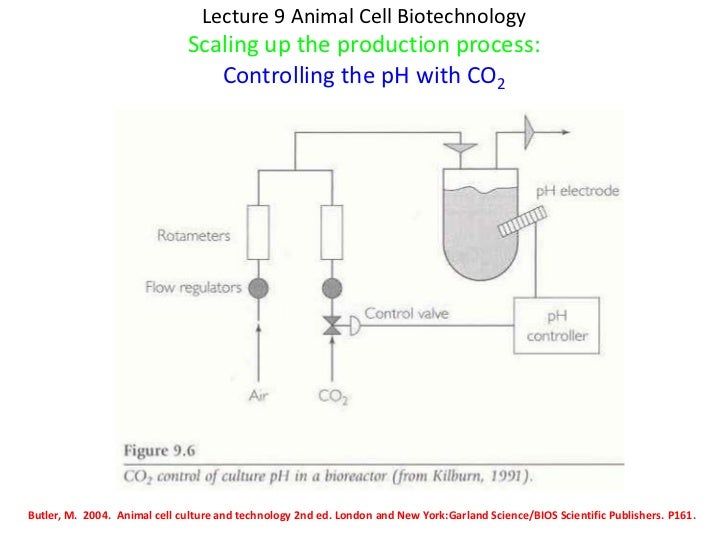
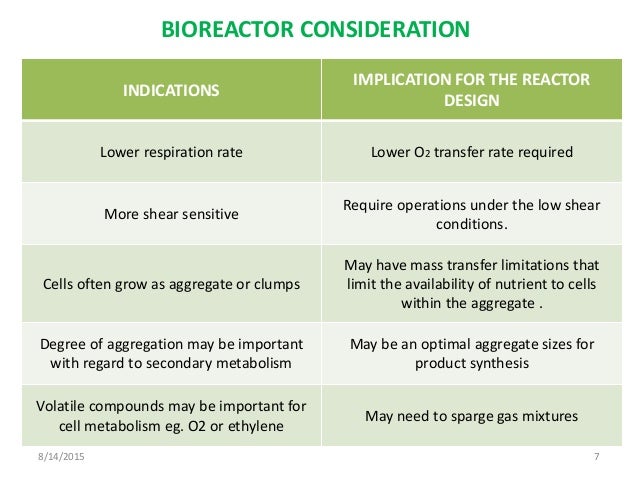
Efficient cell cultivation is dependent on an optimal supply of oxygen and nutrients.
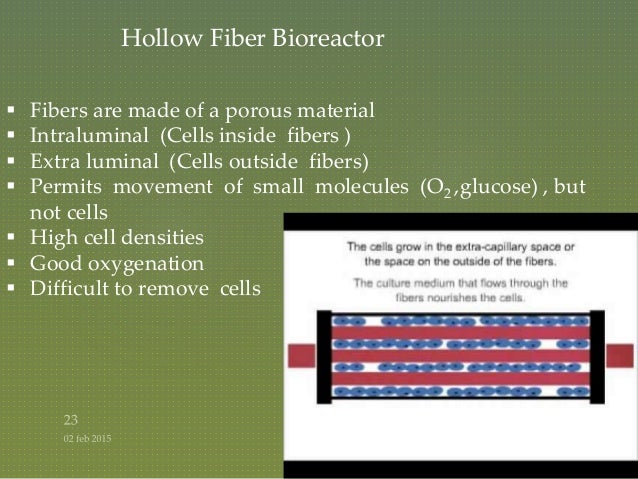
Adherent cell types bind to the hollow fibers and deposit their extracellular matrix and cellular.
The production of monoclonal antibodies on a laboratory scale.
However for its particular nature viscosity of plant cell is low and mixing in airlift bioreactors is not greatly affected by biomass up to 40gl 1 formation of dead zones where conditions are anoxic and cells settle out is a problem.
Growth of animal cells in a suspension celline bioreactor the is a disposable two compartment cultivation device suitable for many cell culture applications.
In one case a bioreactor is a vessel in which a chemical process is carried out which involves organisms or biochemically active substances derived from such organisms.